
I’m Dr Mark Ashton Smith, a cognitive neuroscientist trained at the Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition (a joint programme between the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University). I was a Lecturer and researcher in the Psychology Department at the University of Cambridge, and I am currently a Lecturer in Cognitive Psychology & Neuroscience at the University of Essex Online. I’ve spent the last two decades working on cognitive interventions and on a specific question most “brain training” never answers properly: How do you get gains that show up outside the app, in real decisions and real pressure?
In the past few years, ideas from computational cognitive neuroscience have helped clarify the design principles that matter. I synthesised these into a computational framework called Trident G, which guides how we build training loops that aim for far transfer, not just practice effects.
You can connect with me on LinkedIn here.
I maintain a Substack scientific blog which you can subscribe to for free here (or click on the icon!)
Why IQ Mindware Training Works
Most brain training improves performance on tasks that look like the training. That is not the same thing as becoming better at thinking in daily life.
So our method is built around two coordinated targets that must work together outside the lab:
- Fluid reasoning (IQ-relevant skill): solving unfamiliar problems, spotting structure, updating models fast.
- Cognitive resilience: staying clear, steady, and effective when stress, emotion, fatigue, or setbacks hit.
And we don’t ask you to “take it on faith”. We track change using a Core Test Set at the start and end of a programme, so you get an honest before/after picture.mpact our combined training delivers.
What we measure
The Core Test Set (Start → End)
- Reasoning Snapshot: a short, culture-fair reasoning check (pattern/logic) to track fluid thinking.
- Cognitive Resilience Check: a brief, validated measure of how you recover, persist, and stay effective under load.
- Decision Habits Challenge: a short measure of everyday decision patterns under pressure (how you choose, delay, avoid, or act).
These are chosen because they map onto the Trident G view that performance is not just “raw horsepower”, but control within a usable band: the ability to think clearly and keep thinking clearly when conditions are noisy. You can think of this as being ‘in the zone’ when efficiency, productivity and flexibility peaks.
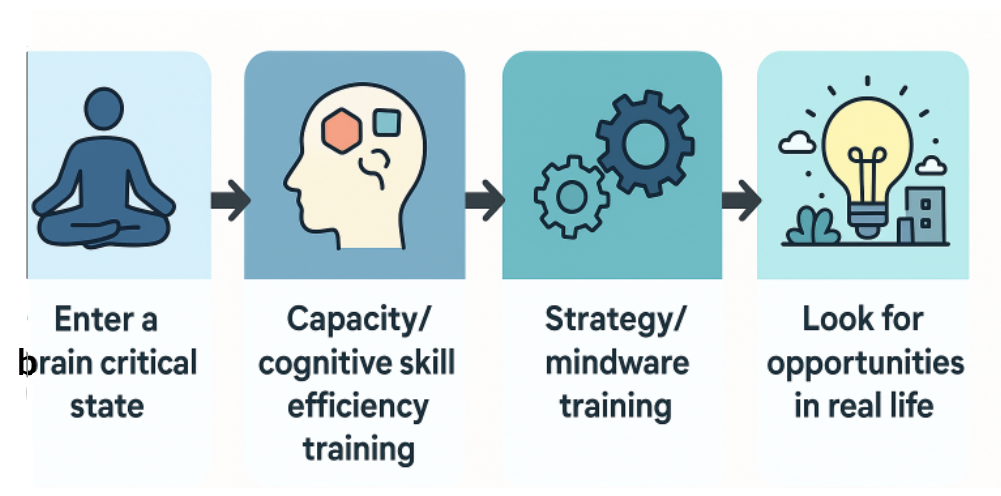
The Training Protocol
Think of IQ Mindware as a four-step daily loop:
1) Enter “The Zone” (2–3 minutes)
You start with a short breathing or coherence exercise to shift into relaxed, motivated alertness.
In Trident G terms, the goal is to stabilise the conditions under which learning is most efficient: not dull and flat, not overwhelmed and frantic, but ready.
Choice:
- If you feel tense or scattered, do the calming version.
- If you feel flat or sluggish, do the energising version.
2) Capacity & Cognitive-Skill Training (15 minutes)
This is where we stretch the “core machinery” that supports fluid reasoning and attentional control, using adaptive N-back style training (difficulty adjusts so you’re challenged but not overwhelmed).
Built-in learning features
- Immediate feedback (so errors become learning signals, not confusion).
- Adaptive difficulty (so the task stays inside a productive challenge range).
- Interference-control elements (so you practise filtering “near misses” and distraction).
3) Strategy & Mindware Training (5–10 minutes)
Capacity alone does not guarantee far transfer. So we add short, practical thinking tools that you practise directly.
Examples include:
- Problem decomposition: turning a vague problem into a concrete plan.
- Decision control under uncertainty: how to compare options when outcomes are unclear.
- Metacognition: knowing when to persist, when to switch tactics, and how to recover after mistakes.
This is where IQ Mindware differs from “just brain games”: we deliberately pair capacity drills with usable operators you can run in your real environment.
4) Real-Life Transfer Prompt (2 minutes)
At the end of each session you write one short transfer note:
- Where will I use this today?
- What situation will trigger it?
- What will I do when it triggers?
This is a small step, but it matters. It turns training into behavioural deployment, not just performance inside the app.
Our Three Signature Games
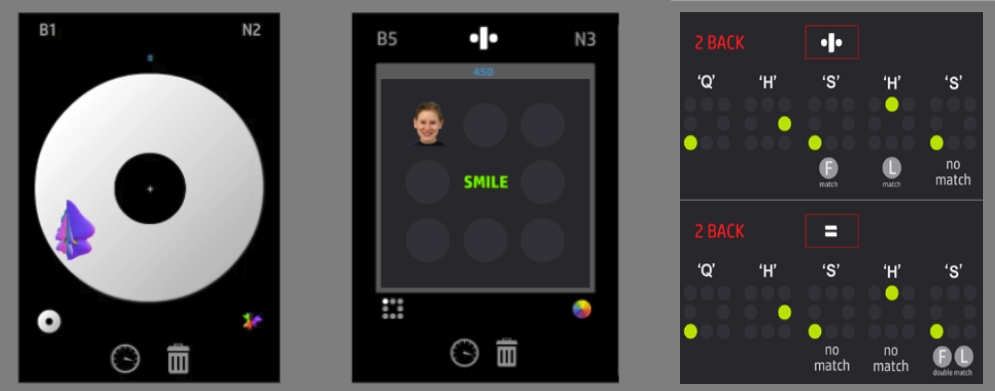
Episodic Dual N-Back (Cognitive Maps for Fluid Reasoning)
Instead of repeating the same simple stimuli, sessions use varied, information-rich material so you’re not just rehearsing one narrow trick. The intent is to strengthen flexible updating and the kind of structured “mapping” that supports reasoning when the situation is new.
Logic-Gated Dual N-Back (Relational Reasoning Under Load)
This version adds a rule layer to working memory. On each trial, your response is gated by a logical operator such as AND / OR / XOR, so you are not only tracking items, but also computing relations between them. The intent is to train relational processing and rule-based updating, which are central to fluid reasoning in real-world problem solving.
Emotional Dual N-Back (Resilience Under Interference)
Here the “noise” is emotional or stress-relevant distraction. You practise staying on-task when your attention is being pulled.
In plain English: you train clarity with noise present, because that is what real life demands.
What Should Change in Real Life
We’re explicit about transfer. The goal is not “you’ll feel smarter”. The goal is that you notice concrete shifts such as:
- You hold more of a discussion/problem in mind before losing the thread.
- You spot structure faster when a task is unfamiliar.
- You recover more quickly after a mistake, interruption, or stressful trigger.
- You make decisions with less avoidance and more deliberate comparison.
Think about the following:
- When a meeting gets fast and you start to lose the thread…
- When you feel the “stress spike” and want to rush or avoid…
- When you’re stuck and looping on the same plan…
What Goes Wrong (and How to Recover)
If sessions start to feel too hard: reduce difficulty for one day and complete the loop cleanly (Zone → Game → Strategy → Transfer). Consistency beats heroics. ΨG-Writing Protocol
If you miss days: do not “catch up” with marathon sessions. Restart with one short loop. The aim is stability and re-entry, not punishment.
Track Your Gains
Across the programme, you can track a simple five-axis profile aligned with Trident G:
- Fluid reasoning (g / IQ-relevant)
- Cognitive resilience (r)
- Brain-state stability (“in the zone” consistency)
- Metacognition (χ): monitoring, switching, strategy control
- Self-efficacy (η): confidence that effort works and you can recover
These are not abstract concepts. They are the levers that determine whether improved capacity becomes usable intelligence in your real context.
References
Ariës, R. J., Groot, W., & Maassen van den Brink, H. (2015). Improving reasoning skills in secondary history education by working memory training. British Educational Research Journal, 41(2), 210–228.
Ashton Smith, M. (2023). The FEP+ Model of General Intelligence. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/65gzh
Ashton Smith, M. (2025, November 28). Life on the Cusp: The Trident G Theory of General Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/kv43n_v3
Ashton Smith, M. (2024b). Strategy-Capacity Training: An Intervention Method for Effective Far Transfer. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/z6fjt
Ben Izhak, S., & Lavidor, M. (2023). Strategy and core cognitive training effects on working memory performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Cognition and Development, 24(2), 207–228.
Chan, S., Mueller, U., & Masson, M. (2019). Far-transfer effects of strategy-based working memory training. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1285.
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
Erk, S., Kleczar, A., & Walter, H. (2007). Valence-specific regulation effects in a working memory task with emotional context. NeuroImage, 37(2), 623–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.041
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., & Perrig, W. J. (2008). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(19), 6829–6833. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801268105
Li, B., et al. (2016). Combined cognitive training vs. memory strategy training in healthy older adults. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 834.
Mather, M., & Sutherland, M. R. (2011). Arousal-biased competition in perception and memory. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6(2), 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691611400234
Momennejad, I., Russek, E. M., Cheong, J. H., Botvinick, M. M., Daw, N. D., & Gershman, S. J. (2017). The successor representation in human reinforcement learning. Nature Human Behaviour, 1, 680–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-017-0180-8
Morrison, A. B., & Chein, J. M. (2011). Does working memory training work? Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18(1), 46–60. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-010-0034-0
Ochsner, K. N., & Gross, J. J. (2005). The cognitive control of emotion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(5), 242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2005.03.010
Owen, A. M., McMillan, K. M., Laird, A. R., & Bullmore, E. (2005). N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20131
Partanen, P., et al. (2015). Metacognitive strategy training adds to the effects of working memory training in children with special needs. International Journal of Psychological Studies, 7(3), 130–140.
Yassa, M. A., & Stark, C. E. L. (2011). Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends in Neurosciences, 34(10), 515–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2011.06.006
Veloso, G. C., & Ty, W. E. G. (2021). The Effects of Emotional Working Memory Training on Trait Anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 549623. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.549623


